Hair Science, Hair Biology, Our Hair
THE STRUCTURE OF YOUR HAIR
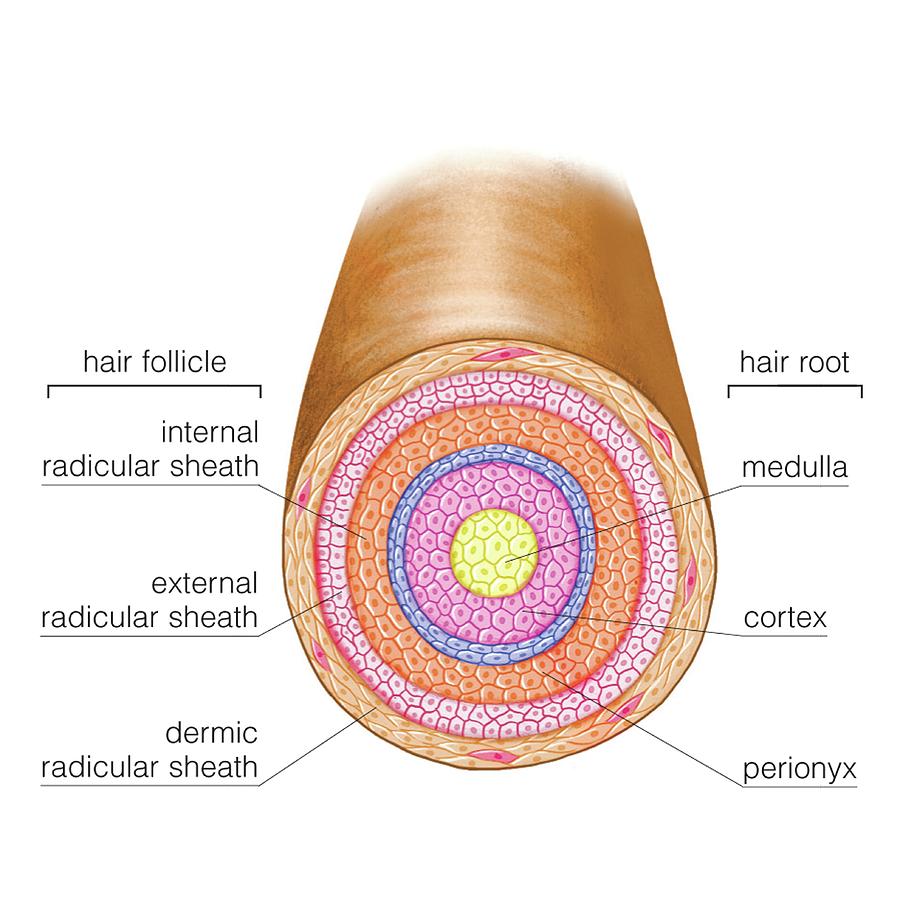
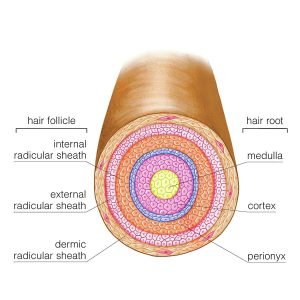 Our hair structure is mainly made up of the tough protein keratin. However, our hair fibres have a structure that consists of several different layers.
Our hair structure is mainly made up of the tough protein keratin. However, our hair fibres have a structure that consists of several different layers.
The three different layers are the cuticle, which consists of several layers of flat, thin cells. The cortex, which contains the keratin, bundled in a cell-like structure and the medulla, a disorganised and open area at the fibre’s centre.
Each layer plays a part in the characteristic of our hair. The medulla is not always present and is an open, unstructured region. The cortex, or middle layer of the hair, is the primary source of mechanical strength and water uptake. The cortex contains melanin, which colours the fibre and determines the colour of your hair, based on the number, distribution and types of melanin granules. The shape of these follicles determines the shape of the cortex, and the shape of the fibre relates to how straight or curly your hair is People with straight hair have round hair fibres, and people with oval and other shaped fibres tend to have more wavy or curly hair. The cuticle is the outer covering of the hair, its structure slides as the hair swells and is covered with a single molecular layer that makes the hair repel water.
Classification Systems
To determine what your hair type is there are various systems that help people classify their curl patterns. It is important to know what your hair type is as it is a good way to know how susceptible to damage your hair is and in turn, how to care for your hair properly.
The Andre Walker System is the most widely used system to classify hair. The system shows four categories of hair types, all with subcategories that go into more detail.
Hair type 1: Straight hair
Type 1 is straight hair, which reflects the most sheen and also resilient of all the hair types. Straight hair is very hard to damage, and also difficult to curl. This is because the sebum in this hair texture easily spreads from the scalp to ends without curls or kinks, and is also the oiliest hair type.
Hair type 2: Wavy hair
Wavy hair has a texture and sheen between straight and curly hair and is likely to become fizzy. Fine wavy hair can be tamed and easily styled, however, medium and coarse hair can be hard to style.
Hair type 3: Curly hair
Type 3 is curly hair, which, is known to have an S-shape. The pattern of the hair resembles an ‘S’ shape and sometimes a ‘Z’ shape. This type of hair is usually voluminous, climate dependent, and damage prone. If your curly hair lacks proper care you can cause less defined curls.
Hair type 4: Kinky hair
Kinky hair features a tightly coiled curl pattern is often very fragile with a high density. This type of hair shrinks when wet because it has fewer cuticle layers than other hair types and because of this, is more susceptible to damage. These are the 4 main types of hair, all of which come with subcategories (see table below). The subcategories go more in depth to the type of hair, what it looks like, how susceptible to damage it is and how easily it is to tame and style.
(Table source)
Knowing your hair type
Knowing your hair type is very important as it can help you decide what is the best way to care for your hair. Your lifestyle and how you care for your hair can help with your growth cycle, and in some cases help to reduce the risk of hair loss. ( source HSC)